Within the framework of geo-Q we are building a sensitive torsion balance (TB) facility that will be constructed and operated in a dedicated laboratory in the new HITec building. It will provide a high precision test facility for the development of novel optical gravitational sensor concepts that are also being investigated within our collaborative research center. Addionally, we plan to use our facility to test components for future drag-free space missions, which all require drag-free test masses, which must be carefully protected from all spurious non-gravitational forces such as electrostatic surface effects, magnetic fields, gas damping force noise, etc. These spurious forces need to be measured in order to develop sensor systems that are free from their disturbances.
When aiming for a quasi-free motion along one degree of freedom and measuring small forces and torques, torsion balances have been the instruments of choice. While the basic principle to measure in an observation frame orthogonal to the vertical axis, in which Earth’s gravitational pull is the dominant effect, seems pretty straight forward and simple, the requirements with respect to intrinsic and ambient noise sources are challenging in TB experiments.
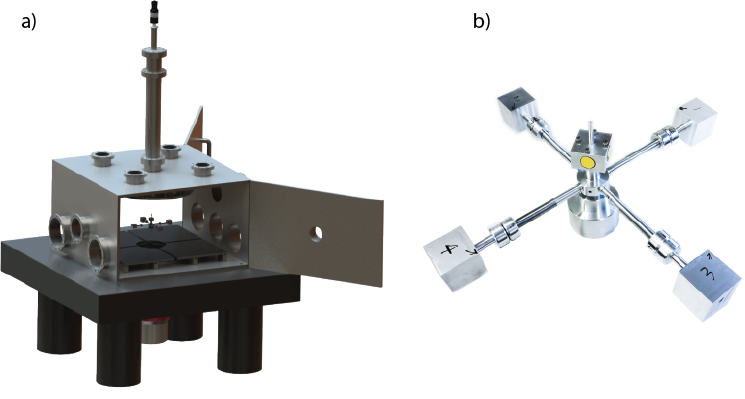
Figure 01a is a CAD drawing of our TB. A vacuum setup including a pump system and a stainless steel tank with a nominal pressure of 10-8 mbar was designed to accommodate a 1m torsion fiber and a 4-arm payload with identical copies of mock-up test masses (see figure 01b). While typically capacitive sensors are used to read out the interesting degrees of freedom, within the framework of project A06 we are studying the system integration of laser-interferometric readout technologies and optomechanical accelerometers to improve the readout sensitivity, stability and controllability of torsion balances. In order to sense and later control the torsional operating point, a stray light immune optical lever readout system based on a modulation demodulation technique was developed. Besides this, further subsystems such as heavy-duty piezo actuators to counteract seismic noise, and electrostatic actuators for adjustment of the rotational degree of freedom are being investigated. Our aim is to achieve an ultra-low-force environment such that small spurious forces acting on test masses can be investigated, and low-noise optical sensors (A07) can be tested.
Principal Investigators
Callinstr. 38
30167 Hannover
Callinstr. 38
30167 Hannover
Callinstr. 38
30167 Hannover
Callinstr. 38
30167 Hannover